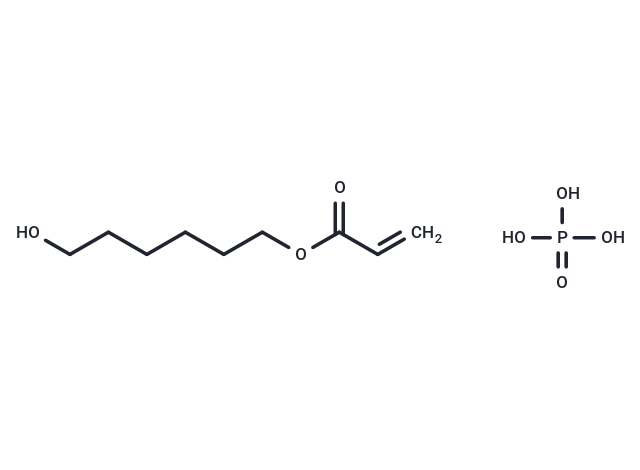
6-Acryloyloxyhexyl phosphate
CAS No. 125200-63-7
6-Acryloyloxyhexyl phosphate( —— )
Catalog No. M34677 CAS No. 125200-63-7
6-Acryloyloxyhexyl phosphater (PA21) is a novel phosphate-binding agent, which is an iron-based reagent, and can be used for the treatment of hyperphosphatemia in chronic kidney disease.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 445 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 686 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 938 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 1398 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1822 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name6-Acryloyloxyhexyl phosphate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description6-Acryloyloxyhexyl phosphater (PA21) is a novel phosphate-binding agent, which is an iron-based reagent, and can be used for the treatment of hyperphosphatemia in chronic kidney disease.
-
Description6-Acryloyloxyhexyl phosphater (PA21) is a novel phosphate-binding agent, which is an iron-based reagent, and can be used for the treatment of hyperphosphatemia in chronic kidney disease.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number125200-63-7
-
Formula Weight270.218
-
Molecular FormulaC9H16O3 xH3O4P
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO=C(OCCCCCCO)C=C.O=P(O)(O)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Rhaponiticin
Rhaponticin(Rhaponiticin) can alleviate liver steatosis and improve blood glucose and lipid profiles in KK/Ay diabetic mice, indicates that rhaponticin has a noticeable antidiabetic effect.
-
1,3-Propanediol
1,3-Propanediol is a natural product produced by microbial fermentation of glycerol.
-
Methyl ganoderate D
The fruit body of Ganoderma lucidum.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


